Artificial Intelligence in Supply Chain

Supply chains have grown to be more complex, data-rich, and vulnerable in this interconnected world. They remain susceptible to disruptions from natural disasters, geopolitical shifts, or sudden demand surges, leading to costly stockouts and delays. To manage this intricacy, companies are increasingly adopting Artificial Intelligence (AI).
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming supply chain management (SCM) by processing vast datasets from IoT sensors to social media, uncovering patterns, predicting outcomes, and automating real-time decisions. This enables companies to achieve more accurate demand forecasting, optimized inventory, smarter supplier negotiations, and precise logistics orchestration.
This article synthesizes foundational concepts, real-world examples, benefits, challenges, and practical steps for implementing AI in supply chains and logistics. It is crafted for management students who aspire to lead in an era where AI is not just an enabler but a strategic imperative.
How Does AI in Supply Chain Work?
AI in supply chains operates by ingesting, processing, and acting on vast volumes of structured and unstructured data. Here’s a view of its inner workings:
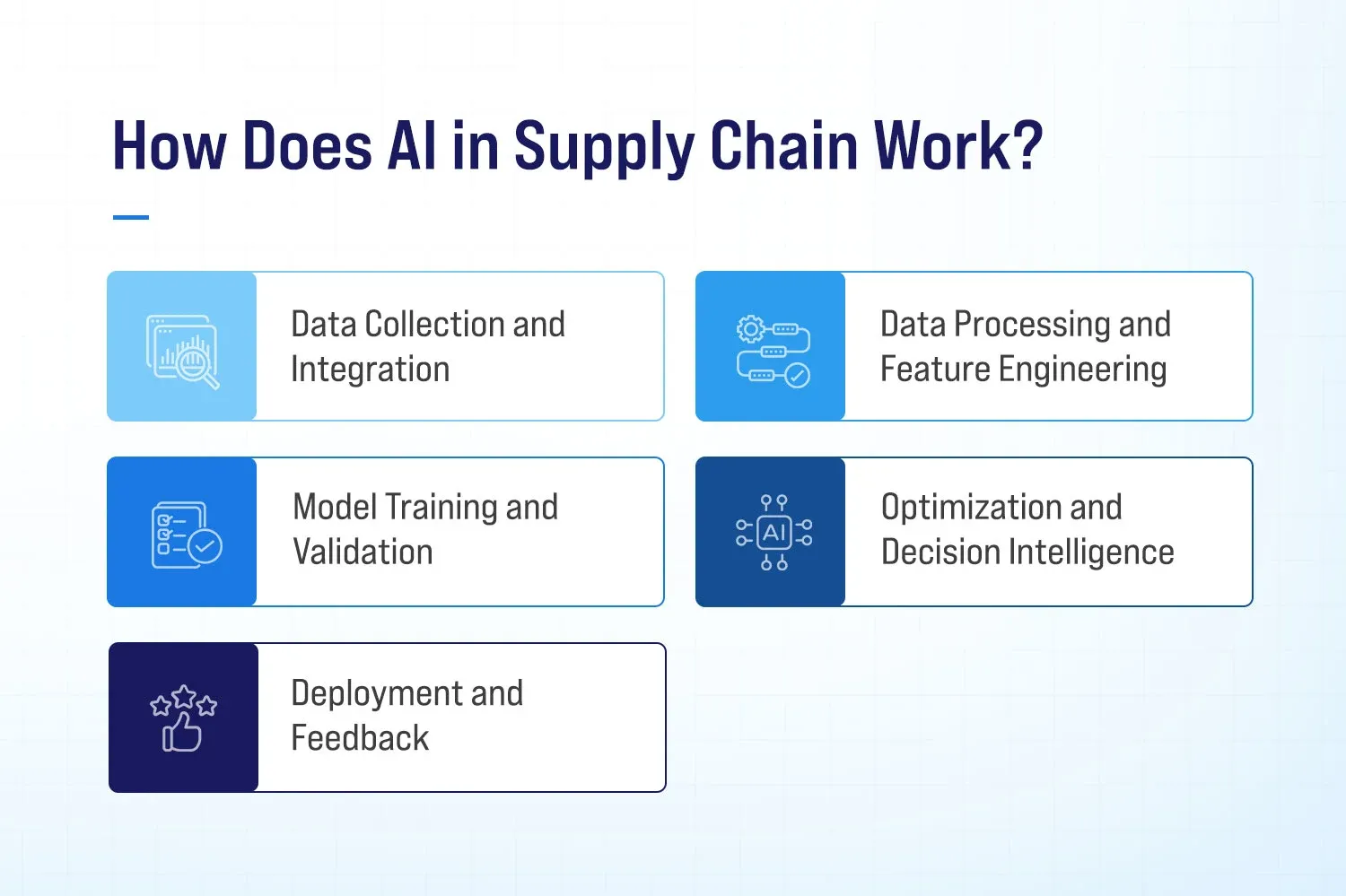
Data Collection and Integration
- Sources: Enterprise systems (ERP, WMS, TMS), Internet of Things (IoT) sensors (temperature, humidity, equipment status), transactional records, social media feeds, weather and traffic data, market indicators, and regulatory updates.
- Integration: Data is aggregated into a unified platform, often a cloud-based data lake where it is cleaned, normalized, and tagged with contextual metadata.
Data Processing and Feature Engineering
- Processing: AI systems address gaps in data, anomalies, and irregular formats for cleaner inputs.
- Feature Engineering: Specialists and data scientists work together to transform raw data into insightful variables (features). For example, “supplier lead-time variance” or “average temperature deviation in transit.”
Model Training and Validation
- Machine Learning (ML): Supervised models (e.g., random forests, gradient boosting) learn to forecast demand, detect anomalies, or classify supplier risk based on historical labeled data.
- Unsupervised Learning: Clustering and dimensionality reduction algorithms identify hidden patterns—such as grouping similar suppliers or detecting unusual logistics behaviors.
- Generative AI (Gen AI): Large language models and simulation engines generate textual summaries (“what-if” scenario narratives), alternative product designs, and automated negotiation scripts.
Optimization and Decision Intelligence
- Optimization Algorithms: Mixed-integer programming and heuristic solvers optimize production schedules and inventory levels and recommend the best routes for delivery to reduce costs and risks.
- Prescriptive Analytics: AI systems not only predict (“What will happen?”) but also recommend actions (“What should we do?”), ranking alternatives by cost, risk, and service-level impacts.
Deployment and Feedback
- Operationalization: AI models integrate with user interfaces like dashboards, chatbots, and mobile apps—or directly feed automated control systems (e.g., warehouse robotics and automated procurement bots).
- Continuous Learning: Real-time data streams update model parameters, while human feedback (e.g., overriding a suggestion) retrains and refines algorithms to improve accuracy and trust.
By automating data-intensive tasks and augmenting human judgment, AI systems enable supply chain managers to focus on high-value strategic decisions.
AI in Supply Chain Management Examples
Let's understand AI in supply chains with examples:
- Demand Forecasting with ML: A global electronics retailer uses ML models that ingest POS data, promotional calendars, and social-media sentiment to predict SKU-level demand. Forecast accuracy improved by 25%, reducing both stockouts and excess inventory.
- Automated Procurement Negotiation: A major consumer-goods corporation deployed a Gen AI-powered “procurement co-advisor” to conduct first-round supplier negotiations. The AI bot handled price and lead-time discussions, shortening negotiation cycles by 40% and cutting procurement costs by 5%.
- Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing: A machinery producer deployed IoT sensors on assembly lines, using ML to analyze vibration and heat patterns, forecasting breakdowns two weeks early and cutting unplanned halts by 30%.
- Smart Warehouse Management: A leading e-commerce company employs AI-driven robotics coordination. Computer vision systems direct autonomous mobile robots on optimal pick paths, boosting picking efficiency by 35% and decreasing order fulfillment times.
- Dynamic Route Optimization: A last-mile logistics provider integrates real-time traffic, weather, and delivery-priority data into its routing engine.AI dynamically adjusts delivery routes, achieving a 20% drop in transit times and a 15% decrease in fuel usage.
- Digital Twin Simulations: A pharmaceutical supply chain uses a digital twin to mirror its end-to-end network. Gen AI simulates potential disruptions—such as regulatory changes or raw-material shortages—and prescribes mitigation strategies, improving resilience planning.
These examples illustrate AI’s versatility—from predictive tasks like forecasting and maintenance to generative applications such as negotiation and simulation.
Benefits of AI in Supply Chains
AI brings transformative benefits to supply chain operations by enhancing decision-making, increasing efficiency, and reducing operational risks. By harnessing machine learning, predictive insights, and automation, AI makes supply chains more adaptive, robust, and customer centric. Below are the key benefits:
Lowering Operating Costs
AI helps organizations significantly reduce operational expenses by identifying inefficiencies, streamlining repetitive tasks, and minimizing manual intervention. By automating functions like order processing, inventory tracking, and demand forecasting, AI reduces labor costs, eliminates redundancies, and ensures resources are allocated more effectively. This results in a leaner, more cost-efficient supply chain.
Making Advanced Real-Time Decisions
AI enables real-time decision making by processing large volumes of data instantly and offering intelligent insights. This allows supply chain managers to respond rapidly to disruptions, shifts in demand, or supplier issues. With access to current and historical data, AI-powered systems provide actionable recommendations that improve responsiveness and strategic agility.
Cut Down on Errors and Waste
One of AI’s core strengths is its ability to detect patterns and anomalies that human operators might overlook. By continuously monitoring supply chain activities, AI minimizes human errors in tasks such as inventory reconciliation, order fulfillment, and shipment tracking. It also reduces waste by optimizing production schedules, material usage, and storage, leading to more sustainable operations and fewer costly mistakes.
Tailoring Inventory Management
AI enhances inventory management by offering highly accurate demand forecasts and replenishment plans. It synchronizes stock with live sales patterns and buyer behavior, preventing excess inventory and shortages while enhancing service quality.
Improving Warehouse Efficiency
AI-driven systems boost warehouse efficiency through smarter space utilization, optimized picking paths, and automated task scheduling. Machine learning models analyze data to configure layouts, predict incoming volumes, and prioritize workflows. As a result, warehouses can handle more throughput with fewer delays and higher accuracy, improving productivity across operations.
Enhancing Supply Chain Sustainability
Sustainability is increasingly important in modern supply chains, and AI contributes by enabling more resource-efficient planning and operations. It can reduce carbon emissions by optimizing transportation routes, consolidating shipments, and minimizing returns. AI promotes ethical procurement by improving transparency, ensuring suppliers meet sustainability criteria.
Optimizing Operations Through Simulation
AI empowers supply chain managers with simulation and modeling tools that replicate real-world scenarios and predict the impact of potential decisions. Digital twins and simulation models help organizations test different strategies—such as new delivery routes, supplier changes, or production shifts—before implementation. This proactive approach reduces risk, enhances strategic planning, and supports continuous improvement.
What Are the Challenges of AI in Supply Chain?
While AI can revolutionize supply chains, deployment comes with hurdles. Adopting AI requires significant planning, investment, and cultural shifts. Organizations must navigate both technical and strategic obstacles to ensure successful integration. Below are the key challenges involved:
Downtime for Training
Introducing AI into a supply chain involves more than deploying new technology—it requires people to adapt to new tools and workflows. Employees require training to operate, interpret, and oversee AI tools competently. During this transition, temporary disruptions in operations are likely. This downtime can impact productivity and performance, especially if not properly managed through phased implementation and change management strategies.
Startup Costs
Adopting AI often demands significant initial capital. Costs can include the purchase or development of AI software, cloud infrastructure, data integration tools, and training programs. Additionally, organizations may need to hire specialized talent or consult external experts. These financial barriers can be particularly challenging for smaller businesses or those with limited digital infrastructure.
Complexity of AI
AI systems are inherently complex. They require integration with existing IT architecture, coordination across multiple departments, and constant data input to function correctly. Maintaining and fine-tuning these systems demands ongoing technical expertise. Without proper oversight, the complexity can lead to inefficiencies, underperformance, or breakdowns in communication between human and machine interfaces.
AI Risks
Inaccuracy of Data
AI's accuracy hinges on training data as flawed, obsolete, or skewed data produces unreliable outputs. In the supply chain context, this can result in misaligned inventories, delayed shipments, or incorrect demand forecasts. Ensuring data quality, consistency, and transparency is essential, yet often difficult due to the vast and varied sources of supply chain data.
Overreliance on AI
Overdependence on AI carries strategic hazards, as it lacks human intuition, discernment, and interpersonal abilities. When organizations delegate too many decisions to AI without human oversight, they risk becoming vulnerable to system errors, unforeseen anomalies, or disruptions that require human problem-solving capabilities. AI should complement, not supplant, human decision-making.
Security and Privacy Vulnerabilities
AI systems handle massive amounts of confidential data, from trade secrets to consumer records, making them prime targets for hackers and leaks. Weak safeguards can lead to severe legal penalties, financial losses, and brand damage. Additionally, growing regulatory demands force firms to align AI operations with privacy laws and ethical standards, introducing further operational challenges.
AI in Supply Chain Management for Different Industries
Artificial intelligence is not a one-size-fits-all solution; its value lies in how it's adapted to meet the specific demands of different industries. Each sector uses AI to solve unique logistical and operational challenges, enabling smarter, more agile, and customer-focused supply chains. Here’s how AI in logistics and supply chain is transforming operations across a range of industries:
Retail
In the retail sector, AI acts as a digital analyst, interpreting purchasing behavior and sales data to anticipate customer demand. This helps retailers fine-tune their stock levels, avoiding the costly consequences of overstocking or running out of high-demand products. Additionally, AI supports procurement teams by identifying optimal suppliers and even aiding in negotiation strategies, making sourcing more strategic and efficient.
Food and Beverage
Supply chains in the food and beverage industry face the added pressure of managing perishable inventory. AI assists by monitoring environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity to ensure quality preservation during storage and transit. Moreover, predictive algorithms help align supply with consumer demand, reducing spoilage and ensuring that fresh goods like dairy and produce are replenished precisely when needed.
eCommerce
For eCommerce platforms, speed and accuracy are essential. AI enhances fulfillment operations by orchestrating warehouse activities and delivery processes. From managing robotic systems that handle inventory picking to planning delivery routes for maximum efficiency, AI helps eCommerce businesses achieve faster shipping times and reduce human error, leading to better customer satisfaction.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, AI helps manage the intricacies of global supply chains, particularly those involving thousands of components like engines, brakes, and electronic modules. AI automates parts ordering, balances inventory levels, and synchronizes deliveries to manufacturing plants. This keeps production efficient without the expense of surplus inventory.
Healthcare
AI plays a critical role in healthcare logistics by forecasting the need for essential medical supplies and pharmaceuticals. By analyzing patterns in healthcare usage and tracking inventory levels, AI ensures that critical items such as vaccines, medications, and surgical equipment are delivered where and when they’re needed. This is critical in crises where swift supply access is lifesaving.
Fashion
In the fast-moving world of fashion, AI helps brands keep up with evolving consumer tastes and seasonal shifts. It analyzes trend data to forecast which styles will be in demand and aligns procurement and manufacturing schedules accordingly. From sourcing raw materials to coordinating global distribution, AI helps fashion businesses deliver new collections on time while minimizing inventory risks.
Steps to Prepare a Supply Chain for AI
Introducing artificial intelligence into a supply chain requires more than just installing new software—it demands strategic planning, organizational alignment, and continuous adaptation. Here are key steps firms must follow to ready their supply chains for AI adoption.
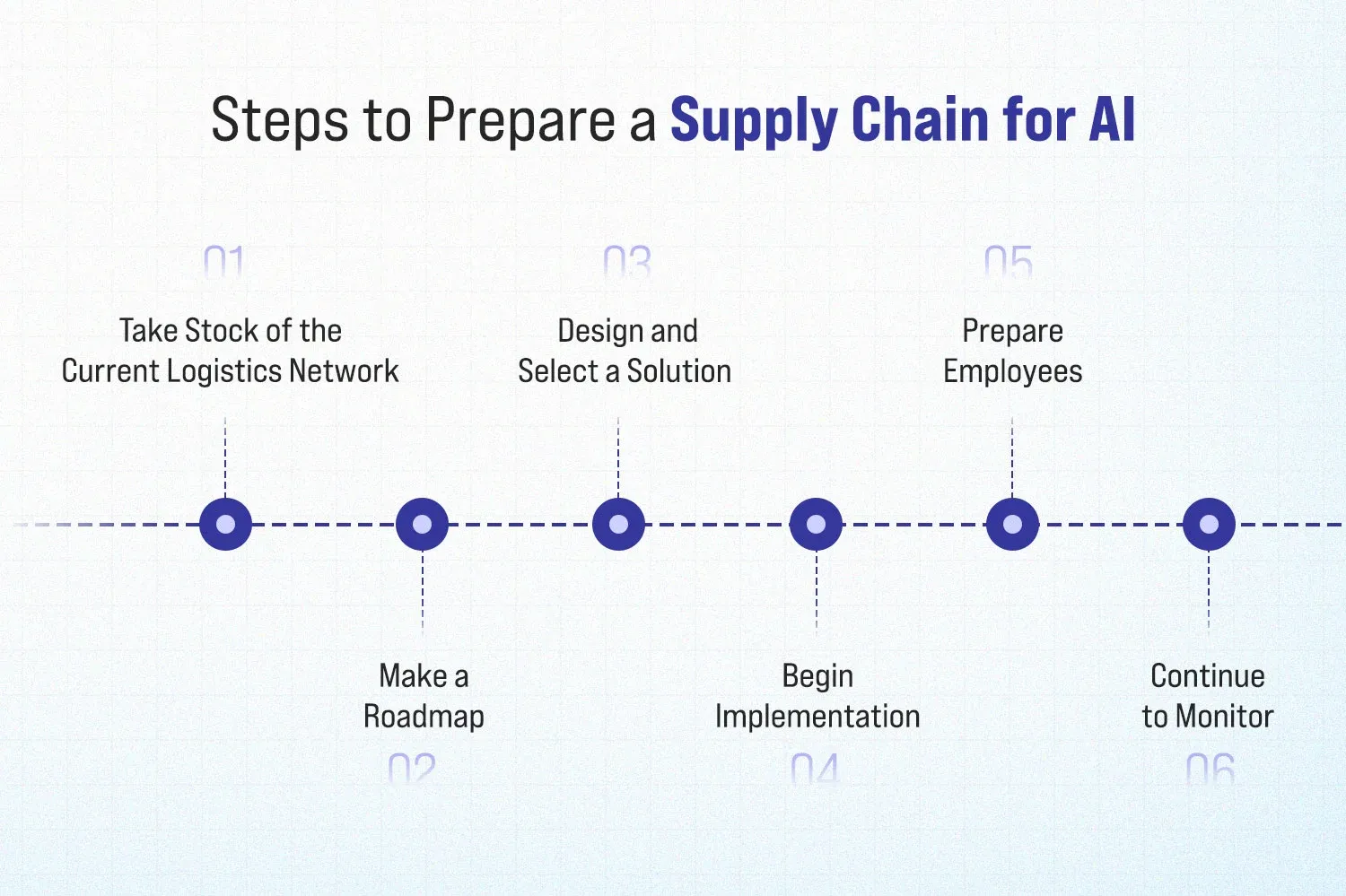
Take Stock of the Current Logistics Network
The first step is understanding the existing supply chain operations from end to end. This includes evaluating processes such as inventory management, procurement, warehousing, transportation, and customer fulfillment. Identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas where data is lacking helps create a foundation for where AI can deliver the most value. It's important to audit both structured (e.g., database) and unstructured (e.g., emails, documents) data to ensure it is accurate and accessible for AI systems.
Make a Roadmap
Once the current system has been analyzed, the next step is to develop a clear roadmap that outlines how AI will be introduced. This includes setting short-term and long-term goals, prioritizing areas for improvement, and identifying measurable success indicators. The roadmap should be aligned with business objectives—whether that’s reducing costs, improving service levels, or enhancing sustainability.
Design and Select a Solution
Not all AI tools are created equal, and the right solution depends on the supply chain’s specific challenges and goals. At this stage, businesses must explore different AI technologies such as predictive analytics, machine learning models, and automation platforms and evaluate which ones best fit their needs. This often involves collaborating with technology vendors or consulting with AI experts to ensure compatibility with existing systems.
Begin Implementation
Implementation marks the beginning of bringing AI into day-to-day operations. Initial efforts typically target a single segment, like demand prediction or automated warehousing. During this phase, businesses must coordinate between internal teams (like IT and operations) and external vendors to integrate the new system seamlessly.
Prepare Employees
Successful AI implementation requires employee buy-in and training. Employees must grasp both the technology’s mechanics and its role in improving their workflows. Clear communication about the purpose of AI, along with hands-on training, helps reduce resistance and ensures smooth adoption. Upskilling teams to work alongside AI tools is critical for long-term success.
Continue to Monitor
AI systems are not “set and forget” solutions. They require continuous monitoring and maintenance to ensure they are operating effectively. As the business environment changes, AI models need to be updated and retrained using fresh data. Ongoing assessments pinpoint further refinements and ensure alignment with shifting supply chain objectives.
FAQs
Q1. What is the future of AI in supply chain?
Ans: AI will make supply chains smarter, faster, and more resilient. It will enhance real-time decision-making, automated operations, and improve demand forecasting, leading to more efficient and adaptive supply networks.
Q2. What companies use AI in supply chains?
Ans: Many global companies use AI in their supply chains, including Amazon, Walmart, Unilever, Maersk, and Nike. They use AI for demand projections, automated storage, route planning, and stock control.
Q3. How does Amazon use AI in their supply chain?
Ans: Amazon uses AI to automate warehouses, optimize delivery routes, predict product demand, and manage inventory efficiently; enabling fast, accurate, and large-scale order fulfillment.
Summing Up
Artificial intelligence has moved from theory to reality, reshaping supply chain operations today. By enabling faster decisions, predictive insights, and smarter automation, AI empowers businesses to navigate today’s complex and volatile supply environments with greater confidence and agility.
However, maximizing AI’s benefits demands more than mere technological integration. It demands a clear strategy, quality data, the right talent, and a willingness to embrace change. For future business leaders and supply chain professionals, understanding how to harness AI responsibly and effectively will be key to building resilient, efficient, and sustainable supply chains.

