What is an eCommerce Business?

In a world defined by convenience, speed, and endless connectivity, eCommerce has fundamentally transformed the way we buy and sell. It all began in August 1994, when 21-year-old Dan Kohn and three classmates at Swarthmore College launched NetMarket—one of the internet’s very first commerce sites—and his friend Phil Brandenberger purchased a copy of Sting’s Ten Summoner’s Tales for $12.48 plus shipping, secured by state-of-the-art encryption.
This pioneering sale ignited a revolution that has since grown into a trillion-dollar digital marketplace and a cornerstone of the global economy. But what exactly is an eCommerce business, and what does it take to launch and sustain one? In this article, we’ll unpack the fundamentals, mechanics, and best practices for building a thriving eCommerce venture.
What is eCommerce?
At its core, electronic commerce (eCommerce) represents the digital exchange of products and services through online platforms. Instead of visiting a physical store, customers browse product catalogs, place orders, and make payments through websites, mobile apps, social media platforms, or online marketplaces. Transactions encompass a wide spectrum, including:
- Retail sales of physical goods (apparel, electronics, home goods).
- Digital products (software, e-books, online courses).
- Subscription services (streaming media, software-as-a-service).
- Financial services (online banking, insurance).
- Auctions and peer-to-peer exchanges (used goods, collectibles).
eCommerce spans everything from retail storefronts (B2C) and wholesale supply (B2B) to peer-to-peer exchanges (C2C) and subscription services, making it a versatile, 24/7 channel for commerce worldwide.
The goal of an eCommerce business is to leverage technology to reach customers efficiently, facilitate secure transactions, and provide seamless fulfillment—from order placement to delivery or digital access.
How Does eCommerce Work?
eCommerce brings together multiple technologies and processes to create a seamless online shopping experience—from the moment a customer discovers a product to the final delivery (or digital access) and beyond. At a high level, here’s how the major components interact:
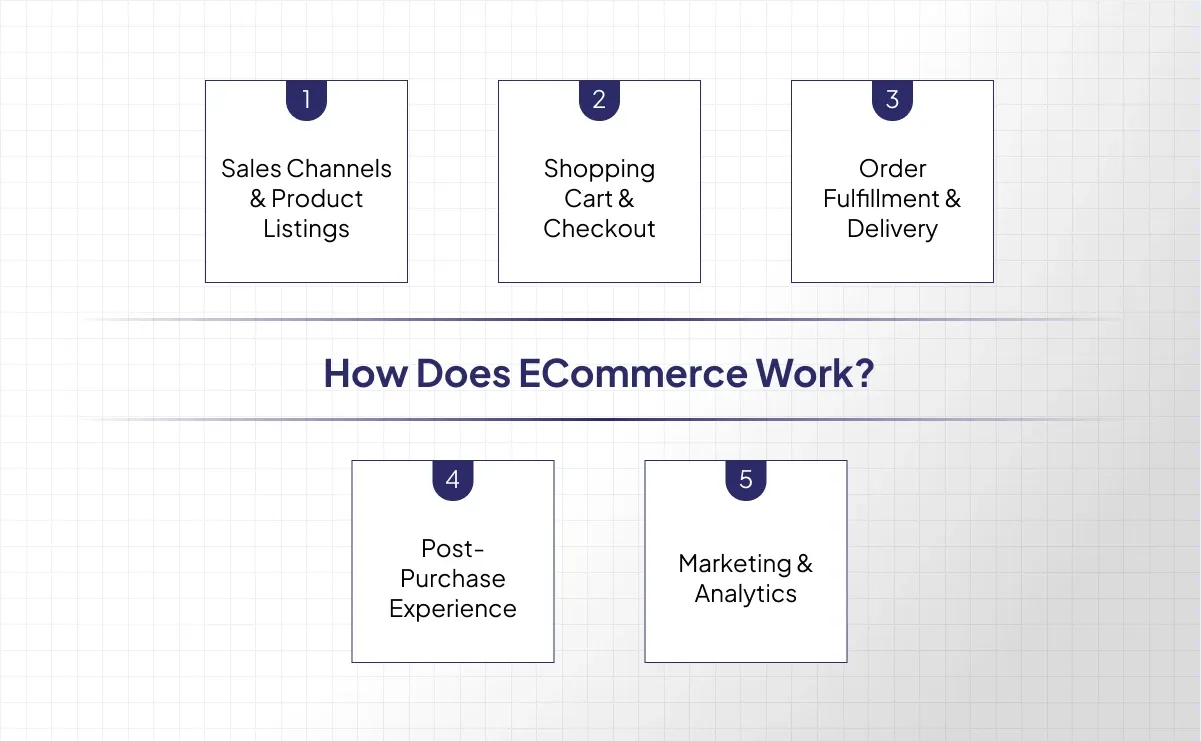
Sales Channels & Product Listings
- Platforms: Sellers choose one or more channels to showcase their offerings—such as a dedicated website (Shopify, WooCommerce), an online marketplace (Amazon, Etsy), or social-commerce integrations (Instagram Shopping, Facebook Shops).
- Catalog Management: Each product is described with images, detailed specifications, pricing, and inventory levels. Retailers enhance product visibility by optimizing listings for search engines and improving on-site navigation to streamline customer access.
Shopping Cart & Checkout
- Cart Functionality: Interested shoppers add items to a virtual cart, adjust quantities, and review totals. Smart features often suggest complementary products (cross-sells) or upgrades (upsells).
- Secure Checkout: At purchase time, customers enter shipping information and select a payment method. Payment gateways (e.g., Stripe, PayPal, Shop Pay) encrypt card or wallet data to process transactions safely, meeting industry standards like PCI DSS.
Order Fulfillment & Delivery
- Inventory Management: Inventory tracking systems automatically adjust stock quantities the moment a purchase is made.
- Logistics: Depending on models like self-fulfillment, dropshipping, or third-party logistics (3PL), the order is packed, labeled, and shipped. Buyers get instant updates on shipment status through automated emails or text messages.
Post-Purchase Experience
- Customer Support: After delivery, support channels (live chat, email, phone, or AI chatbots) handle returns, exchanges, and inquiries, ensuring satisfaction and fostering loyalty.
- Feedback & Engagement: Businesses solicit reviews, offer loyalty programs, and send personalized follow-up communications (e.g., product usage tips, replenishment reminders) to encourage repeat purchases.
Marketing & Analytics
- Traffic Generation: Digital marketing tactics, including SEO, content marketing, paid ads (Google Ads, Facebook Ads), and influencer partnerships, drive potential customers to the store.
- Data-Driven Optimization: Performance metrics such as visitor origins, sales conversion, order value, and repeat customer revenue are monitored using analytical tools. Sellers use these insights to refine product offerings, pricing, and promotional strategies.
By orchestrating these interconnected systems like sales platforms, payment security, fulfillment networks, customer service, and marketing analytics, eCommerce businesses can deliver a convenient, 24/7 shopping experience to customers around the globe.
Types of eCommerce
eCommerce encompasses a variety of models defined by who’s buying from whom. Grasping these critical differences enables entrepreneurs to select the most suitable operational framework for their commercial endeavors. The eCommerce landscape comprises six fundamental categories.
Business-to-Business (B2B)
B2B commerce involves transactions between corporations, where manufacturers, wholesalers, and distribution specialists provide merchandise to retail businesses or other organizations. Deals typically include large quantities, customized pricing, and extended purchasing timelines. Examples:
- A software vendor licensing enterprise solution to corporations.
- An automotive assembler purchases components from a parts manufacturer.
Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
When people think of online shopping, they typically imagine the traditional B2C eCommerce model. Companies market products straight to end-users via digital shops. Key characteristics include:
- User-friendly product catalogs with detailed descriptions and reviews.
- Fast checkout experiences supporting credit cards, digital wallets, and buy-now-pay-later options.
Examples: Amazon, Flipkart, and direct-to-consumer (D2C) brands like Casper or Glossier.
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
C2C platforms enable private individuals to trade goods or services through intermediary websites. These peer-to-peer marketplaces facilitate trust and transaction management.
- Platforms: eBay, OLX, Facebook Marketplace.
- Common uses: Reselling second-hand items, collectibles, or homemade crafts.
The platform typically takes a small fee or commission on each sale.
Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
The C2B model reverses conventional sales, with individuals offering expertise or products to companies. Examples include:
- Freelancers offering creative or professional services on gig-based platforms.
- Photographers licensing royalty-free images to companies via stock photo sites.
- Crowdsourcing contests where businesses pay for user-submitted ideas or content.
Business-to-Administration (B2A)
B2A eCommerce covers transactions between companies and government agencies. These typically involve:
- Online procurement portals for submitting bids, tenders, or applications.
- Digital services such as company registrations, licensing, and regulatory filings.
A growing area as governments worldwide invests in e-gov initiatives to streamline public-sector workflows.
Consumer-to-Administration (C2A)
C2A eCommerce covers digital interactions between citizens and government entities. Use cases include:
- Filing taxes or paying fines online.
- Scheduling appointments for public services (e.g., passport renewal, health clinics).
- Accessing educational resources through government portals.
Each eCommerce type serves different customer needs and requires tailored strategies—from pricing and marketing to technology and logistics.
What is an eCommerce Website?
An eCommerce website is a digital storefront that enables individuals and businesses to buy and sell products or services entirely over the internet, rather than through a physical location. At its core, an eCommerce website brings together four critical functions in one unified platform:
Product Catalog & Display
- Showcases physical goods (clothing, electronics), digital products (e-books, software), or services (consulting, online courses).
- Organizes items into categories, subcategories, and collections.
- Provides detailed descriptions, pricing, high-resolution images, and customer reviews.
Order Processing & Shopping Cart
- Customers can select and save multiple products in a digital shopping cart.
- Updates inventory levels in real time.
- Guides customers through a secure checkout flow, collecting shipping information and payment details.
Payment Acceptance
- Payment systems connect with processors to support card transactions, e-wallets, installment plans, or direct transfers.
- Uses SSL encryption and PCI-compliant processes to protect sensitive data.
Fulfillment & Customer Service
- Manages shipping logistics, from printing labels to scheduling pickup with couriers or third-party logistics providers.
- Tracks and communicates order status via email or SMS.
- Handles returns, exchanges, and post-sale support through live chat, email, or phone.
Steps to Starting an eCommerce Business
Launching a successful eCommerce venture requires more than a great idea—it takes careful research, deliberate planning, and consistent execution. Here’s a streamlined roadmap to guide you from concept to launch:
Choose Your Product and Niche
- Define Your Vision: Identify the core problem your product or service solves and how it stands out in the market.
- Research Competitors: Analyze similar businesses: their pricing, marketing tactics, website usability, and customer reviews. Note gaps you can fill or areas to improve.
- Assess Market Viability: Consider demand, potential saturation, and barriers to entry. Ensure your margins can accommodate marketing, fulfillment, and overhead.
Identify Your Target Audience
- Build Customer Personas: Create detailed profiles of your ideal buyers—age, location, income, interests, and online behaviors.
- Understand Motivations: Identify customer pain points and motivations to better influence their purchasing decisions.
- Locate Your Channels: Determine where your audience spends time online—social media platforms, forums, search engines—and plan to meet them there.
Validate Your Idea
- Market Analysis: Gauge market size, trends, and competitor share.
- Product Criteria: Test price points, expected markups, and any regulatory requirements.
- Pilot Testing: Consider small-scale preorders, focus groups, or crowdfunding campaigns to gauge real-world interest and collect early feedback.
Develop Your Business Model
Choose a Fulfillment Strategy:
- Self-manufacturing: Produce and ship items yourself.
- Third-party manufacturing: Partner with a factory or white-label supplier.
- Wholesale resale: Buy in bulk and mark up.
- Dropshipping: Have suppliers ship directly to customers.
- Digital products: Eliminate shipping by selling downloads or services.
Create a Business Plan:
- Executive summary
- Company overview and mission
- Market and competitive analysis
- Product/service definitions
- Marketing and sales strategy
- Operational logistics
- Financial projections and funding needs
Register Your Business and Secure Your Brand
Select and Register Your Name: Check availability at your state’s business registry and the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
Obtain Legal Identifiers:
- Claim your domain and social handles.
- Apply for an Employer Identification Number (EIN).
- Secure any required licenses or permits (sales tax, health, safety).
Choose Legal Structure: Seek professional legal counsel to determine whether a sole proprietorship, limited liability company, or corporate structure best suits your operation.
Build Your eCommerce Website
Pick a Platform: Evaluate hosted solutions (Shopify, BigCommerce) vs. self-hosted (WooCommerce, Magento) based on cost, customization, and scalability.
Design With Purpose:
- Purchase and connect your custom domain.
- Create a clean site map prioritizing intuitive navigation.
- Develop a cohesive brand aesthetic—colors, typography,and imagery.
Configure Key Features:
- Product listings should feature crisp images, comprehensive details, and verified buyer feedback.
- Shopping cart and guest account functionality.
- Secure checkout with multiple payment options (cards, wallets, BNPL).
- Shipping settings and tax calculations.
Optimize for Search: Implement on-page SEO—keyword-rich titles, meta descriptions, and alt text—to drive organic traffic.
Develop and Execute Your Marketing Strategy
Multi-Channel Outreach:
- Blog posts and SEO to attract inbound traffic.
- Targeted advertising through Google, Facebook, and Instagram to reach specific demographics.
- Active social media interaction on channels where your customers engage most.
- Influencer partnerships and affiliate programs to extend your network.
Leverage Email & CRM:
- Grow your subscriber base using incentives like free resources or sign-up prompts.
- Streamline initial greetings, cart recovery alerts, and marketing pushes through automation.
- Leverage CRM insights to categorize customers and tailor communications.
Measure and Iterate:
- Monitor essential metrics like visitor behavior, sales conversions, and spending patterns.
- A/B test headlines, layouts, and offers.
- Adjust strategies based on live data and direct customer input.
Following these steps will help businesses launch a resilient, growth-oriented eCommerce business.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of eCommerce?
Here’s a comparison of eCommerce’s key strengths and drawbacks:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
24/7 Accessibility: Customers can shop anytime, anywhere without being restrained by store hours or geographic limits. | High Competition: Low barrier to entry means crowded markets; standing out requires strong branding. |
Global Reach: Sellers can access international audiences without physical storefronts or distributors. | Logistics & Fulfillment: Managing inventory, shipping costs, and returns can become complex and costly. |
Lower Overhead Costs: Eliminates rent, in-store staff, and many utilities, resulting in more spending on marketing. | Dependence on Technology: Technical failures or downtime can disrupt sales and erode consumer confidence. |
Data-Driven Personalization: Track behavior to tailor offers, recommendations, and marketing. | Limited Physical Interaction: The inability to physically inspect products may result in increased return rates. |
Scalability: Easy to add products, explore new markets, or automate operations as you grow. | Security & Privacy Risks: Handling customer data demands robust security measures and compliance. |
How to Succeed in eCommerce?
Success in ecommerce hinges on more than just listing products online—it requires a strategic blend of customer focus, data-driven decision-making, and continuous optimization. Below are five key pillars to help your online store thrive:
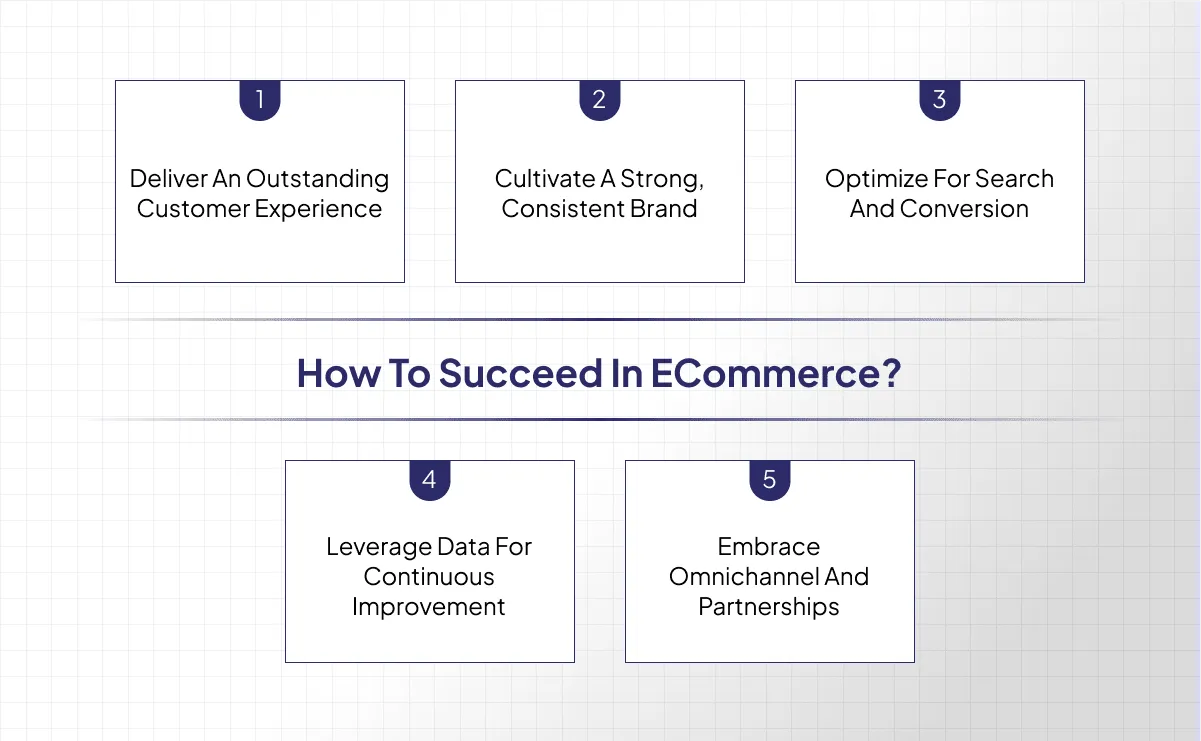
Deliver an Outstanding Customer Experience
- Seamless Website Navigation: Ensure your site’s layout is intuitive, with clear menus, filters, and search functionality so visitors can find what they want in just a few clicks.
- Fast and Reliable Fulfillment: Offer transparent shipping options (standard, expedited, free thresholds) and provide real-time tracking updates. A smooth delivery process builds trust and encourages repeat purchases.
- Responsive Support: Integrate multiple support channels—live chat, email, and phone—and set clear expectations for response times. Enhance customer relationships by acknowledging previous purchases and preferences.
Cultivate a Strong, Consistent Brand
- Distinct Visual Identity: Use cohesive color schemes, typography, and imagery across your website, packaging, and marketing materials so customers instantly recognize your brand.
- Authentic Storytelling: Communicate your brand’s ethos, vision, and product backstory authentically. Be it eco-focus, artisanal quality, or breakthrough ideas, powerful storytelling builds brand loyalty.
- Social Proof: Highlight genuine customer endorsements, case studies, and community-shared content. Seeing real people enjoy your products reinforces credibility and eases purchase anxiety.
Optimize for Search and Conversion
- SEO-Rich Content: Conduct keyword research around your product category and incorporate those terms naturally into product titles, descriptions, blog posts, and metadata. SEO attracts visitors who are actively seeking products or services you provide.
- A/B Testing: Conduct A/B tests on design elements, copy, visuals, and promotional tactics. Even small tweaks—like changing button text from “Add to Cart” to “Buy Now”—can significantly impact conversion rates.
- Mobile-First Design: Optimize for mobile users with responsive layouts, easy navigation, and quick checkout.
Leverage Data for Continuous Improvement
- Analytics Tracking: Use tools like Google Analytics, platform dashboards, and heatmaps to monitor metrics—traffic sources, bounce rates, cart abandonment, and customer lifetime value.
- Customer Segmentation: Group your audience by behavior (first-time vs. returning buyers), demographics, or purchase history. Tailor marketing messages—promotional emails, product recommendations, and retargeting ads—to each segment’s needs.
- Inventory and Pricing Strategy: Analyze sales trends and seasonality to optimize stock levels and avoid stockouts or overstock. Implement dynamic pricing or limited-time promotions to maximize revenue without eroding margins.
Embrace Omnichannel and Partnerships
- Omnichannel Strategy: Expand your retail footprint beyond a single online domain. Expand onto marketplaces (Amazon, Etsy), social commerce (Instagram Shops, TikTok), and even offline pop-ups to meet customers where they already are.
- Influencer Partnerships: Work with creators whose followers match your ideal buyers. Offer special promo codes or referral links to increase visits and sales while growing brand awareness.
- Collaborations and Bundles: Team up with complementary brands for co-branded product bundles or limited-edition drops. Cross-promotions introduce you to new audiences and create a sense of exclusivity.
Summing Up
eCommerce has transformed how businesses operate and how consumers shop, offering unparalleled convenience, global reach, and endless opportunities for innovation. Whether you're launching a B2C brand, scaling a B2B operation, or exploring niche markets, success hinges on understanding your audience, optimizing the customer experience, and leveraging data-driven strategies.
Success in the evolving digital market demands flexibility, ongoing refinement, and openness to innovation. By focusing on value, trust, and seamless execution, you can build a thriving eCommerce business that stands the test of time.

